In this week, we learned about another data structure called binary search tree.A binary search tree is basically a linked list but contains two children nodes. I learned that there exists some special rule for storing data in binary search tree. Also, the lecture covered the material about measuring the performance of algorithms which was once dealt in the previous course CSC108.
As I mentioned above, the binary tree seems to be an extension of linked list that can have maximum of 2 children for each node. There are some important rules involved in inserting and deleting nodes.
- When you are inserting an item to the BST, the position of an item depends on how big it is. If the item is bigger than the root, it must be placed on the right side of root.
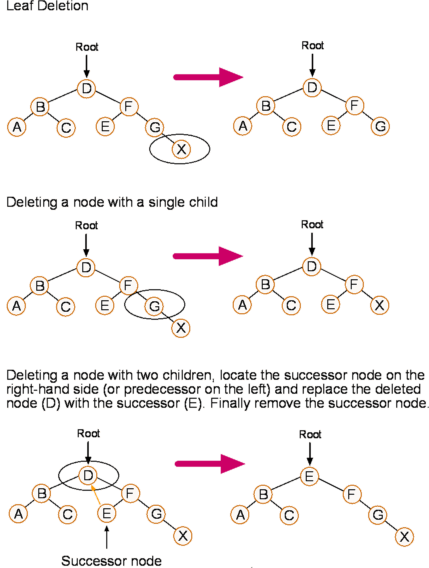
- When you are deleting an item from the BST, it is a little bit more complicated but boils down to three rules. The three rules refer to deleting nodes without any children, nodes with one child, and nodes with two children. If a node has no children, then the node is simply deleted. If the node has one child, then the node is deleted and the child node is brought forward to link to the parent. The complication occurs when a node has two children. However, even here, the rules are straightforward when stated. To delete a node with two children, the next node on the right branch is used to replaced the deleted node. The successive node is then deleted. The successive node will always be the left most node on the right branch.
 |
| from http://www.codeproject.com/KB/recipes/BinarySearchTree/treeDelete1.gif |
No comments:
Post a Comment